TEAM F. Lezoualc’h
SIGNALING AND PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF HEART FAILURE AND AGING
Our team associates researchers and clinicians with a common interest in better understanding the mechanisms involved in heart failure and cardiac aging. Our final goal is to identify relevant drug targets to treat or block the progression of heart failure.
TEAM Members

Frank LEZOUALC’H

Caroline CONTE

Hélène TRONCHERE

Frédéric BOAL

Caterina MICELI

Bertrand MARCHEIX

Clément DELMAS

Olivier LAIREZ

Ezechiel AGBEGBO

Sourour BEN HARZALLAH

Juliette FLORQUIN

Ilias SIMON

Françoise PUJOL

Fraha HAIDAR
New therapeutic targets in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
Karina Formoso, Maximin Détrait, Dorian Bergonnier, Olivier Lairez, Bertrand Marcheix, Clément Delmas, Jean Porterie , Jessica Resta, Yannis Sainte-Marie, Yohan Santin, Frank Lezoualc’h
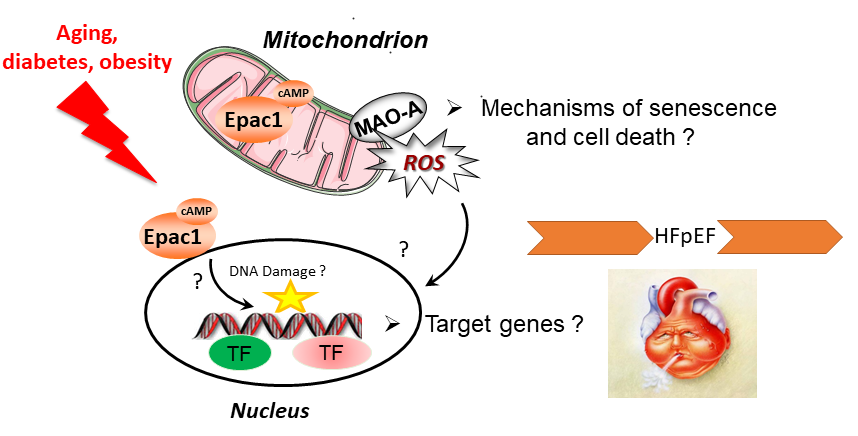
Heart Failure (HF) with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is the most common form of HF and is favored by aging, diabetes and obesity. It is characterized by impaired filling and relaxation of the heart, for which there is no effective therapy. Understanding the mechanisms regulating cardiac remodeling (e.g hypertrophy, senescence, cell death) in the context of diabetes / obesity and aging could pave the way for new treatments of HFpEF. Our team has characterized molecular events that are strongly involved in cardiac remodeling. These “signalosomes” are located in different subcellular compartments and involve the cAMP-sensitive protein, Epac1 or the monoamine oxidase-A (MAO-A). Pioneers in the discovery of these proteins in the heart, we have acquired a strong expertise in these targets and developed a panoply of pharmacological tools and animal models which could allow the development of new therapeutic strategies.
KEY SIGNALING NETWORKS INVOLVED IN THE DEVELOPMENT OF HEART FAILURE AND AGING.
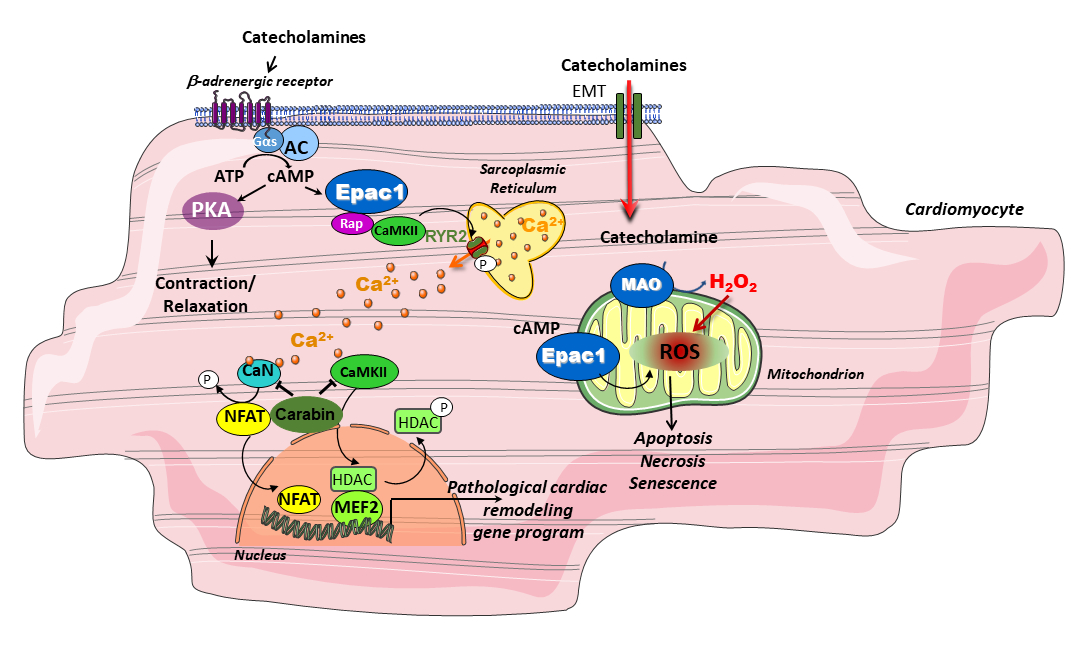
We have identified new signaling pathways involved in heart failure and aging. Our goal now is to dissect the signalosomes of Epac/Carabin/MAO-A proteins in order to under-stand how these proteins influence cell fate. We analyse their molecular events in different compartments of the cardiomyocyte and determine their protein network and target genes. Our approach is multidisciplinary: we are seeking pharmacological modulators of these therapeutic targets and develop new experimental models of HF.
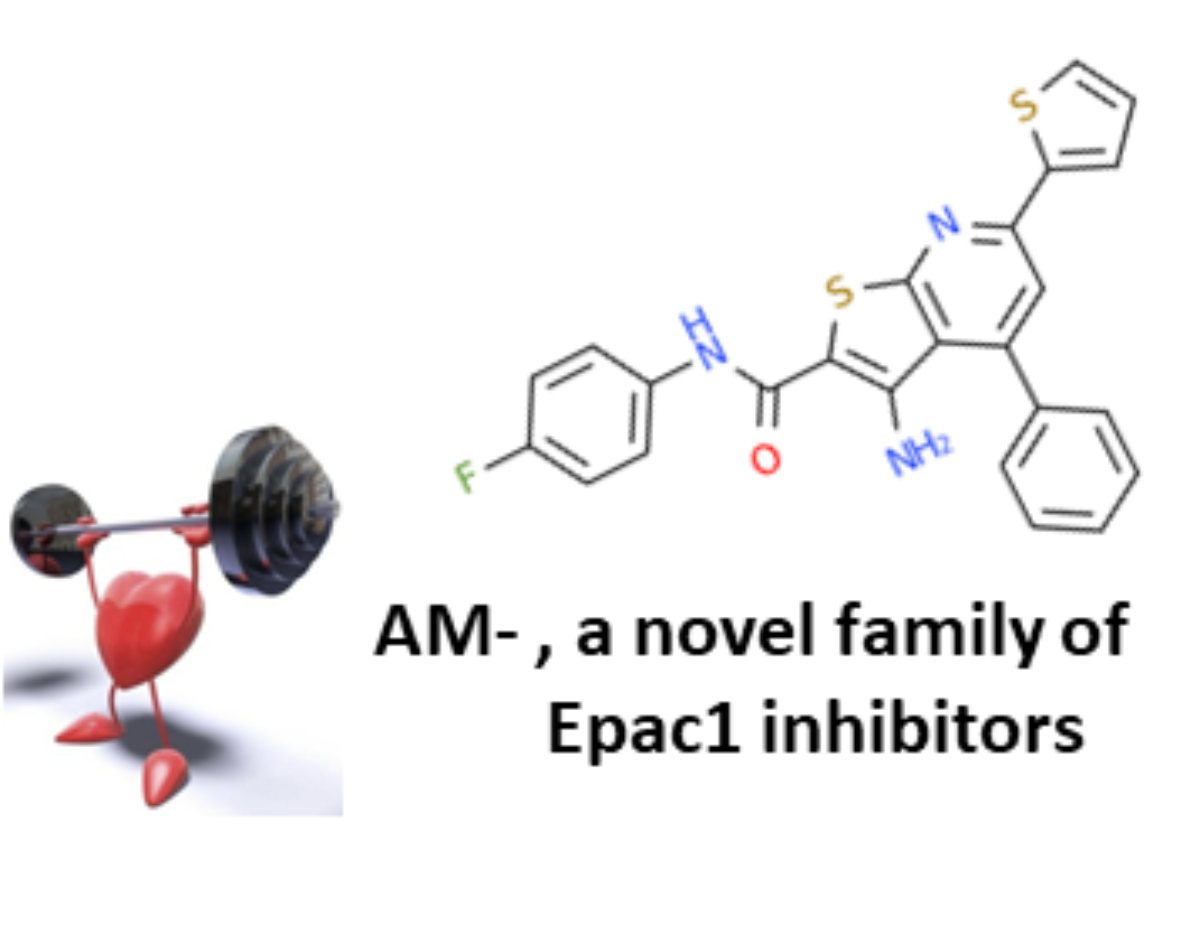
CARDIAC THERAPIES WITH NEW EPAC1 INHIBITORS
Karina Formoso, Maximin Détrait, Olivier Lairez, Clément Delmas , Dorian Bergonnier, Frank Le-zoualc’h
We have provided evidence that Epac1 genetic inhibition is cardioprotective in various cardiac stress condi-tions such as myocardial ischemia. These data suggest that pharmacological inhibition of Epac1 could be beneficial for the treatment of cardiac diseases. To test this assumption, we have established various func-tional tests and have isolated by high through put and virtual screening assays the first two families of Epac1 selective pharmacological inhibitors. The first generation of Epac1 inhibitor named CE3F4 is a tetra-hydroquinoline and behaves as an uncompetitive. The second generation of Epac1 inhibitors named AM- is a subfamily of thieno[2,3-b]pyridine and functions both in vitro and in vivo. We are currently investigating the effect of AM- and CE3F4 in various experimental models of cardiac diseases to test the therapeutic ef-fectiveness of inhibiting Epac1 activity using small-molecule pharmacotherapy.
NANOPARTICLES AS NEW THERAPEUTICS IN HF
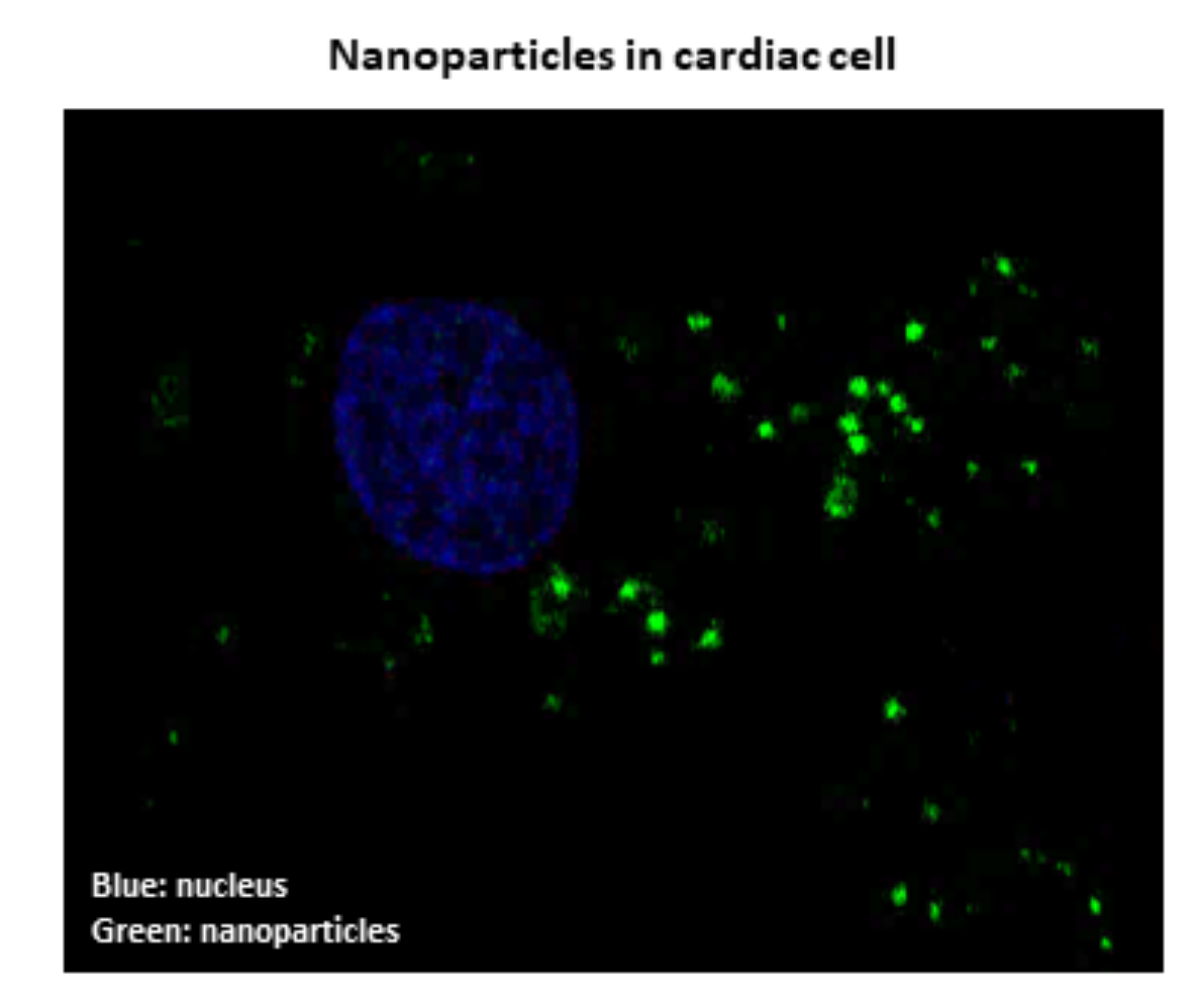
Yohan Santin, Maximin Détrait, Jessica Resta, Frank lezoualc’h
Numerous studies have shown that autophagy, a dynamic process by which damaged intracellular com-ponents are eliminated, is dysfunctional and plays an important role in the development of Heart Failure. Thus, an improvement in autophagy could counter the death of cardiac cells and protect the heart against contractile dysfunction. We are developing nanoparticles that aim at restoring autophagy by acting specifi-cally on lysosomes. Lysosomes are cellular structures that break down damaged material allowing its elimi-nation or recycling. We have shown a good efficiency of these nanoparticles to ameliorate autophagy, and protect cardiac cells from death induced by different stress agents. Our nanoparticles are currently being evaluated for their ability to limit the development of heart failure.
New epigenetic mechanisms in heart failure
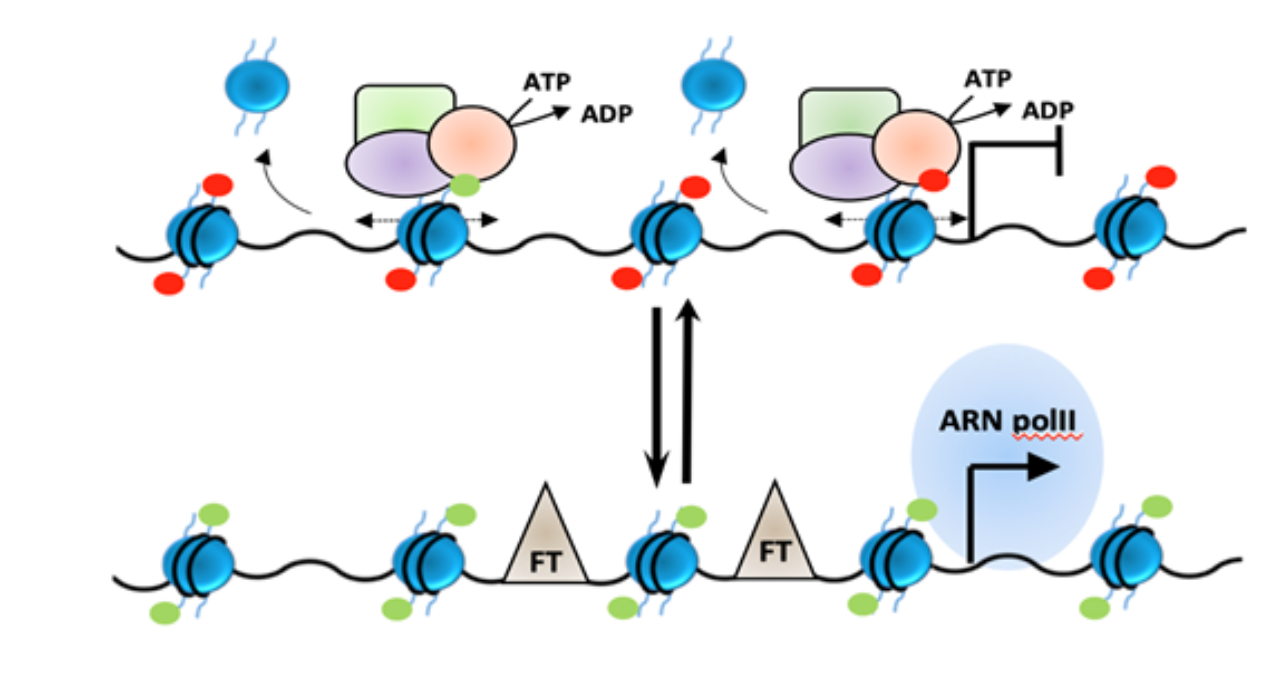
Loubna Kehal, Dorian Bergonnier, Yannis Sainte-Marie, Olivier Lairez, Frank Lezoualc’h, Caroline Conte
Epigenetic markers have recently emerged as key players in the development of cardiovascular disease, suggesting that chromatin modifiers may represent promising targets for the development of new therapies. Cardiac hypertrophy, an early marker in the clinical course of heart failure, is regulated by various signalling pathways that activate a specific gene program characterized by the re-expression of certain fetal genes and repression of genes specific to mature cardiomyocytes. Although a specific epigenetic signature in hyper-trophic cardiomyocytes has been shown, the link between well-characterized signalling pathways and epi-genetic changes is still poorly understood. We have recently identified epigenetic enzymes that modify the histone methylation profiles in cardiomyocytes during cardiac stress. We are trying to understand the impact of these enzymes on gene regulation and the mechanisms regulating their activity and/or recruitment to their target genes in response to cardiac stress.
Selected publications
Mitochondrial 4-HNE derived from MAO-A promotes mitoCa2+ overload in chronic post-ischemic cardiac remodelling.
Santin Y, Fazal L, Sainte-Marie Y, Sicard P, Maggiorani D, Tortosa F, Yücel Yücel Y, Teyssedre L, Rouquette J, Marcellin M, Vindis C, Shih JC, Lairez O, Burlet-Schiltz O, Parini A, Lezoualc’h F and Mialet-Perez J. . Cell Death and Differentiation (2020).. Pubmed
Rational re-design of Monoamine Oxidase A into a dehydrogenase to probe ROS in cardiac ageing.
Giacinto Iacovino L, Manzella N, Resta J, Vanoni MA, Rotilio Laura, Pisani L, Edmondson DE, Pa-rini A, Mattevi A, Mialet-Perez J, Binda C.ACS Chem Biol (2020) . Pubmed
Identification of a pharmacological inhibitor of Epac1 that protects the heart against acute and chronic models of cardiac stress. .
Laudette M, Coluccia A, Sainte-Marie Y, Solari A, Fazal L, Sicard P, Silvestri R, Mialet-Perez J, Pons S, Ghaleh B, Blondeau JP, Lezoualc’h F. Cardiovasc Res. (2019). Pubmed
Monoamine oxidase-A is a novel driver of stress-induced premature senescence through inhibi-tion of parkin-mediated mitophagy.
Manzella N, Santin Y, Maggiorani D, Martini H, Douin-Echinard V, Passos JF, Lezoualc’h F, Binda C, Parini A and Mialet-Perez J.. Aging Cell (2018). . Pubmed
The multifunctional mitochondrial Epac1 controls myocardial cell death
Fazal L, Laudette M, Paula-Gomes S, Pons S, Conte C, Tortosa F, Sicard P, Sainte-Marie Y, Bis-serier M, Lairez O, Lucas A, Roy J, Ghaleh B, Fauconnier J, Mialet-Perez J, Lezoualc’h F. Circ Res (2017) . Pubmed
ILS NOUS SOUTIENNENT










Inserm/UPS UMR 1297 - I2MC Institut des Maladies Métaboliques et Cardiovasculaires
1 avenue Jean Poulhès - BP 84225 - 31432 Toulouse Cedex 4
Tél. : 05 61 32 56 00
Horaires
Du lundi au vendredi
8h30 - 12h30 / 13h45 -16h45
